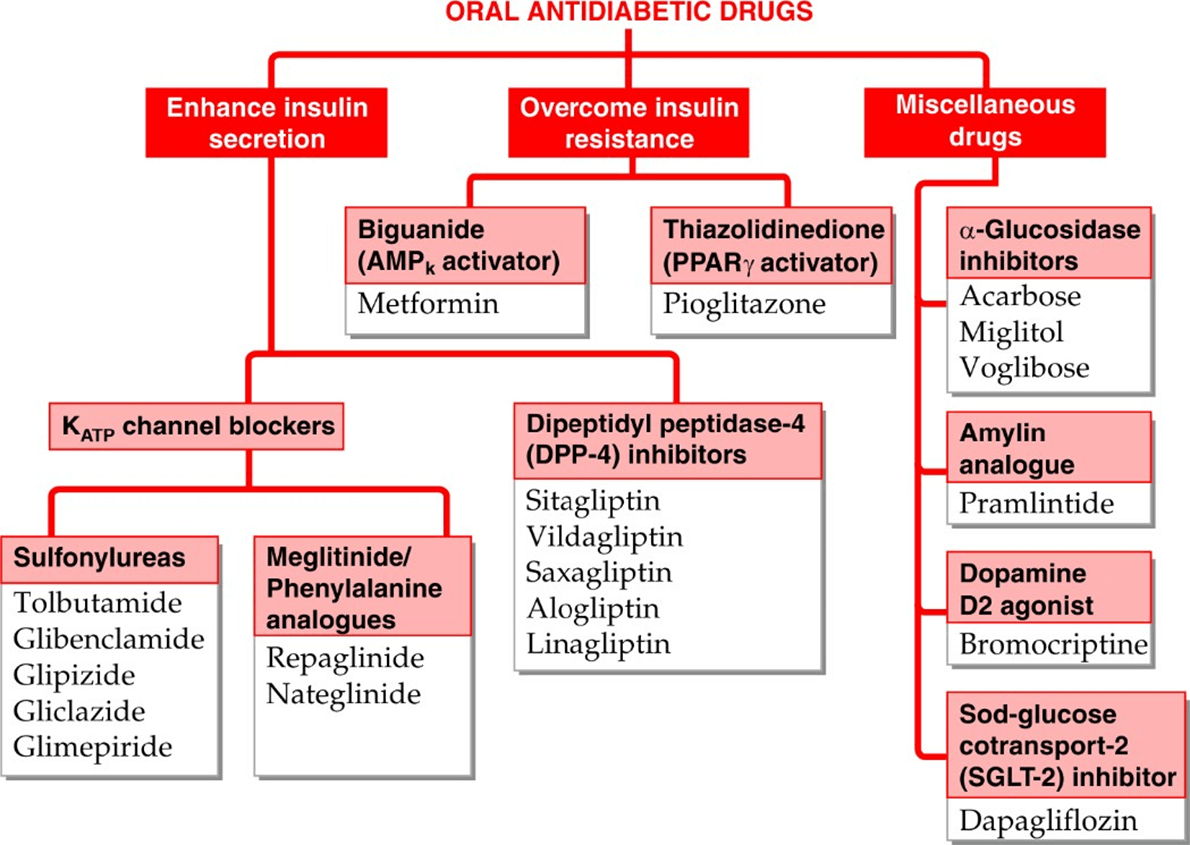
|
Sulphonylureas
|
0.5-1 gm TDS
- Glibenclamide- 5-20 mg OD or BD
|
- Block the Sulfonylurea receptor (SUR1) which constitutes a subunit of the inwardly rectifying ATP-sensitive K+ channel (KATP) in the
membrane of pancreatic β cells.
- The inward flow of K+ ions is thereby restricted, intracellular K+ concentration falls and the membrane is partially depolarized augmenting Ca2+ channel opening as well as release of Ca2+ from intracellular stores.
- The Ca2+ ions promote fusion of insulin containing intracellular granules with the
plasma membrane and exocytotic release of insulin.
|
- Hypoglycemia
- Weight gain
- Hypersensitivity– Rash, photosensitivity, purpura, rarely agranulocytosis
- Disulfiram like action
- Dilutional hyponatremia- chlorpropamide due to ADH like action
- Non- specific side effects– N, V, D, constipation, flatulence, headache, paresthesia
|
- DM
- Diabetes insipidus (Chlorpropamide)
- Diagnosis of insulinomas and diabetes
|
|
Metformin
|
- 500 mg tablet up to 8 tablet per day
- 850 mg BD
|
- Biguanides do not cause insulin release, but presence of insulin is essential for their action.
- Though the details are not clear, recent studies have recognized activation of AMP dependent protein kinase (AMPK) to play a crucial role in mediating the actions of metformin, the key features of which are:
- Suppresses hepatic gluconeogenesis and glucose output from liver. This is the major action responsible for lowering of blood glucose in diabetics.
- Enhances insulin-mediated glucose uptake and disposal in skeletal muscle and fat. Insulin resistance exhibited by type-2 diabetics is thus overcome. This translates into— • glycogen storage in skeletal muscle reduced lipogenesis in adipose tissue and enhanced fatty acid oxidation.
- Interferes with mitochondrial respiratory chain and promotes peripheral glucose utilization through anaerobic glycolysis
|
- GI Side effect- Abdominal pain, anorexia, bloating, nausea, metallic taste, mild diarrhea
- Tiredness
- Metformin does not cause hypoglycemia except in overdose.
- Lactic acidosis
- Vit. B12 deficiency due to interference with its absorption can occur with high dose of metformin.
|
- DOC for all Type II DM except when not tolerated or contraindicated
- PCOS– improve ovulation and fertility
|