|
Theophylline
|
mg tablet up to 8
tablet per day
mg BD
|
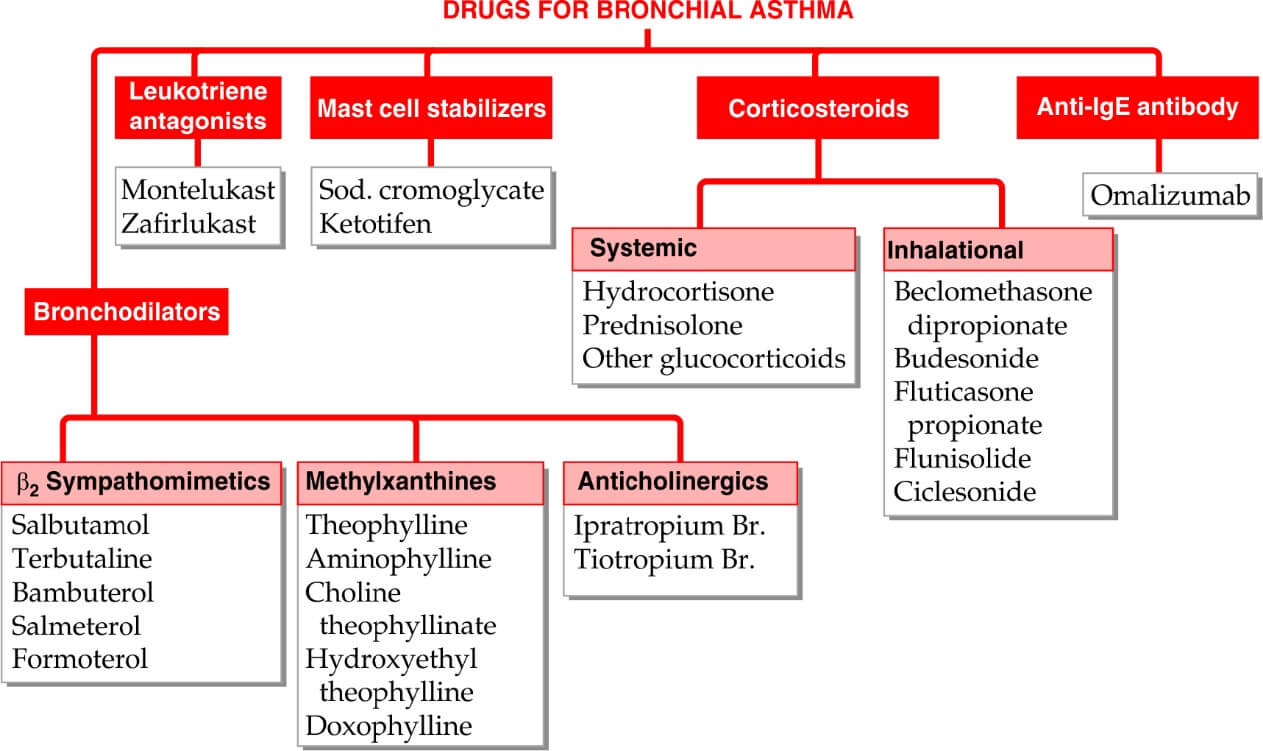
Three distinct cellular actions of methylxanthines have been defined-
- Release of Calcium ion from SR, especially in skeletal and cardiac muscles
- Inhibition of phosphodiesterase (PDE) which degrades cyclic nucleotides intracellularly.
- Blockade of adenosine receptors: adenosine act as local mediator in CNS, CVS- contracts smooth muscle (bronchial), dilates cerebral vessels, depresses cardiac pacemaker and inhibit
gastric secretions
|
- Theophylline has a narrow margin of safety, dose dependent side effects start from upper part of therapeutic concentration (5-20 µg/ml)
- Minimal side effects
- Dyspepsia, headache, nausea, vomiting
- Nervousness, restlessness, tremors, palpitation, diuresis
- Agitation, tachypnea, flushing, hypotension
- Delirium, hypertonia, extra systole
- Convulsion, shock, arrhythmias- due to adenosine A1 receptor antagonism
- Death
|
- Bronchial asthma
- COPD
- Apnea in premature infants
- Cardiac asthma
- Diuretics
- Heart failure
- COPD
- CO2 narcosis
- Cardiopulmonar y resuscitation
- Cheyne’s stokes
respiration
|
|
Anticholinergic
- Ipratropium bromide- short acting (4-6 hrs.)
- Tiotropium bromide– long acting (24 hrs.)
|
|
- Atropinic drugs cause bronchodilation by blocking M3 receptor mediated cholinergic constrictor tone; act primarily on larger airways which receive vagal innervation.
- Presence of M3 receptor on peripheral bronchiolar muscle as well, though they do not have vagal innervation.
|
|
- Severe asthma
- COPD exacerbation
- Smoker asthmatics
- Perennial rhinitis, watery rhinorrhea
|
|
Inhaled corticosteroids
|
|
- Anti-inflammatory
- Anti-allergic
- See steroid
|
Due to inhalation: Hoarseness of voice, dysphonia, sore throat, oropharyngeal candidiasis; can be minimized by using spacer, gargling after every dose; treated by topical nystatin/ clotrimazole
Systemic S/E: only at dose >600 µg/day- see Steroid
|
|