Table of Contents
Classification:

|
Class |
Biological Half Life |
|
Short Acting |
<12 hr. |
|
Intermediate acting |
12-36 hr. |
|
Long acting |
>36 hr. |
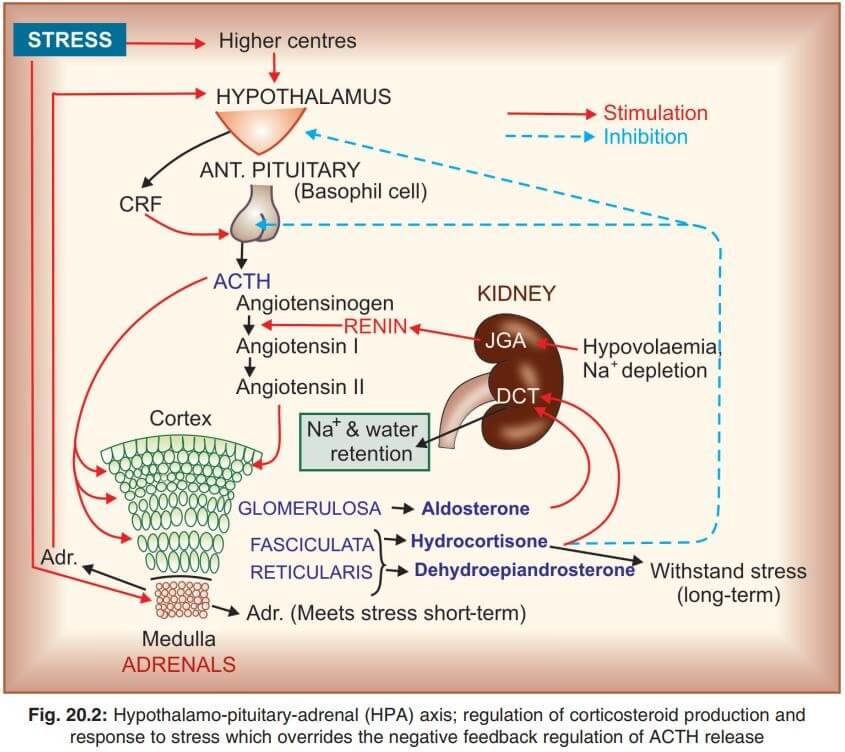
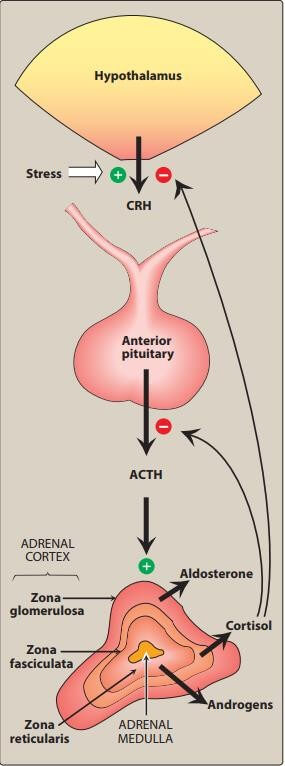
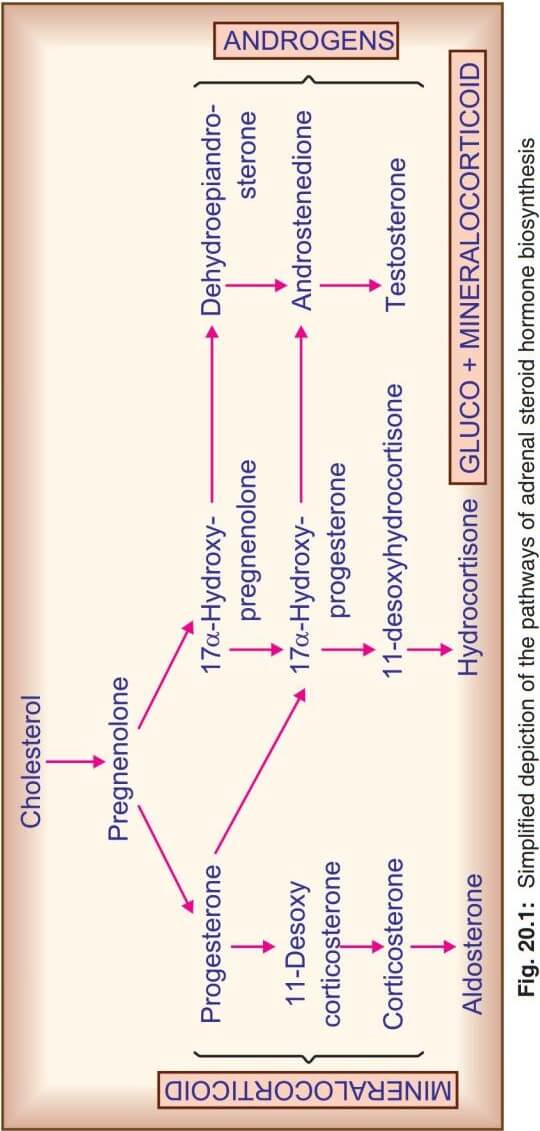
MECHANISM OF ACTION
Most of the known effects of the glucocorticoids are mediated by widely distributed glucocorticoid receptors. These proteins are members of the superfamily of nuclear receptors, which includes steroid, sterol (vitamin D), thyroid, retinoic acid, and many other receptors with unknown or nonexistent ligands (orphan receptors).

All these receptors interact with the promoters of—and regulate the transcription of—target genes.
In the absence of the hormonal ligand, glucocorticoid receptors are primarily cytoplasmic, in oligomeric complexes with heat-shock proteins (hsp). The most important of these are two molecules of hsp90, although other proteins are certainly involved.
Free hormone from the plasma and interstitial fluid enters the cell and binds to the receptor, inducing conformational changes that allow it to dissociate from the heat shock proteins.
The ligand-bound receptor complex then is actively transported into the nucleus, where it interacts with DNA and nuclear proteins. As a homodimer, it binds to glucocorticoid receptor elements (GREs) in the promoters of responsive genes.
In addition to binding to GREs, the ligand-bound receptor also forms complexes with and influences the function of other transcription factors, such as AP1 and NF-κB, which act on non-GRE containing promoters, to contribute to the regulation of transcription of their responsive genes.
These transcription factors have broad actions on the regulation of growth factors, proinflammatory cytokines, etc, and to a great extent mediate the anti-growth, antiinflammatory, and immunosuppressive effects of glucocorticoids.
Two genes for the corticoid receptor have been identified: one encoding the classic glucocorticoid receptor (GR) and the other encoding the mineralocorticoid receptor (MR).
USES
|
Replacement Therapy |
Disease) |
Cushing’s syndrome |
|
Allergic Reactions |
|
|
|
Inflammatory condition of bones and joint |
|
|
|
Collagen disease |
|
|
|
Eye disease |
|
|
|
Pulmonary diseases |
|
|
|
Renal disorders |
| |
|
GI diseases |
disease, UC
|
|
|
Hematological disorders |
|
|
|
Neurological disorders |
|
|
|
Thyroid diseases |
|
|
| ||
|
Infections |
|
|
|
Skin Diseases |
|
|
|
Autoimmune conditions |
|
|
|
Organ transplantation and skin allograft |
(immunosuppression) |
|
|
Nausea and Vomiting |
emetic effects of chemotherapy and general anaesthesia |
|
|
Miscellaneous |
|
|
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Peptic ulcer
- Diabetes mellitus
- Hypertension
- Viral and fungal infections
- TB and other infections
- Osteoporosis
- Herpes simplex keratitis
- Psychosis
- Epilepsy
- CHF
- Renal failure
ADVERSE REACTIONS

|
Mineralocorticoid |
|
|
|
Glucocorticoid |
silent perforation may occur |
|