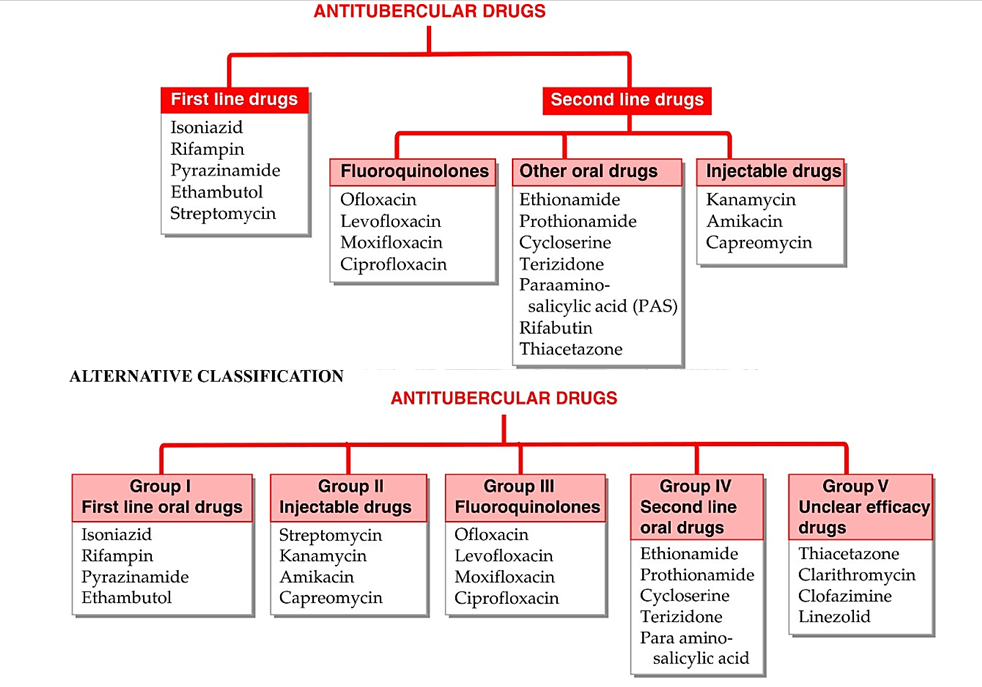
Classification
| Drugs | Dosage | MOA | ADR | USES |
| Isoniazine (Isonicotinic Acid Hydrazide) (H) | § | Tuberculocidal Inhibition of synthesis of mycolic acids which are unique FA component of mycobacterial cell wall. Two gene product labelled ‘InhA’ and ‘KasA’ which function in mycolic acid synthesis are target of INH action. | Peripheral neuritis Paresthesias Numbness Mental disturbances Convulsions These are due to interference with production of active coenzyme pyridoxal phosphate from pyridoxine. Pyridoxine given prophylactically (10 mg/day) prevents neurotoxicity even in higher doses. Hepatitis Lethargy, Rashes, Fever and Arthalgia | TB Completely absorbed orally and penetrate all body tissue, TB cavity, Placenta and meninges |
| Rifampicin (R) | § | Bactericidal- on slowly dividing Rifampicin interrupts RNA synthesis by binding to B- subunit of mycobacterial DNA- dependent RNA polymerase (encoded by rpoB gene) and blocking its polymerizing function. | Hepatitis Flu syndrome- Chills, fever, headache, malaise and bone pain Cutaneous syndrome- flushing, pruritus, rash, redness and watering of eyes Abdominal syndrome- N, V, abdominal cramps, Diarrhea | TB- widely distributed in body, penetrate intracellularly, enter TB cavity, caseous mass and placenta; though crosses meninges- pumped out by P- glycoprotein Leprosy and ENL Prophylaxis of Meningococcal and H. influenzae meningitis and carrier state. MRSA, Dipheroides, Legionella infections Brucellosis- Doxycycline + Rifampicin is DOC Q fever Mycetoma |
| Pyrazinamide (Z) | Tuberculocidal MOA is not well understood Like INH it is also converted inside mycobacterial cell into an active metabolite pyrazinoic acid by and enzyme (Pyrazinamidase) encoded by pncA gene. This metabolite gets accumulated in acidic medium and probably inhibits mycolic acid synthesis, but by interacting with a different FA synthase. Disrupts mycobacterial CM and its transport function. | Hepatotoxicity Hyperurecemia, gout, polyarthalgia- due to inhibition of uric acid secretion in kidney Rashes, fever, flushing Abdominal distress Loss of diabetic control- repeated BG monitoring is warranted | TB- good penetration in CSF, highly useful in meningeal TB | |
| Ethambutol (E) | Tuberculostatic- fast multiplying bacteria MOA not fully understood Inhibit arabinosyl transferases involved in arabinogalactan synthesis thereby interfering with mycolic acid incorporation in mycobacterial cell wall. | Optic neuritis- Loss of visual acuity/ color vision, field of vision Fever Rashes Nausea Peripheral neuritis Hyperurecemia- due to defective urate excretion | TB- penetrate meninges incompletely | |
| Streptomycin (S) | Tuberculocidal but less effective than INH or Rifampicin Acts only on extracellular bacilli due to poor penetration Penetrate tubercular cavity, but do not cross BBB | In case of S-resistance it must be stopped at earliest. Due to narrow margin of safety its use is restricted to maximum of 2 month. Also labelled as supplemental 1st line drugs. | TB- Resistance developed rapidly when used alone in TB |