Table of Contents
THE GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM EXAMINATION
Full GI/Abdominal Examination:
- Introduction, Wash Hands, Consent
- General Inspection:
- Alertedness/Orientation
- ↓ in Hepatic Encephalopathy (Ammonia)
- ↓ in Uraemic Encephalopathy
- Pain/Distress (Acute Abdomen, Appx, Pancrx, Cholecystx, Diverticx, B.Obstrucx, Perforation, etc)
- Body Habitus:
- Obesity (Fatty liver, Diabetes, Ascites, GORD)
- Cachexia (Malignancy, Malabsorption, Crohns/UC)
- Colour:
- Jaundice (Hepatitis, Cholelithiasis, Liver Failure, Cirrhosis, Haemolysis)
- Alertedness/Orientation
-
-
- Pallor (Anaemia, Malignancy, Malabsorption, GI Bleeding)
- Pigmentation (Haemochromatosis)
- Bruising, Bleeding, Petechiae (Liver Failure, Haematological Malignancy)
-
- Vital Signs:
- Pulse:
- Tachycardia (Anaemia, Blood Loss, Pain, Infection)
- AF (Dilated Cardiomyopathy in Alcoholism)
- Blood Pressure:
- Hypertension (Renal Failure, Pain)
- Hypotension (Blood Loss, Shock)
- Postural Hypotension (Anaemia)
- Respiratory Rate:
- Tachypnoea (Pain, Anaemia)
- Temperature:
- Fever (Infection)
- Pulse:
- Hands:
- Perfusion + CRT
- Warm & Sweaty (Carcinoid) + (Hyperthyroid, Phaeox, Acromegaly)
- Cool & Dry (Shock, Hypovolaemia)
- Clubbing (Crohn’s Disease & Ulcerative Colitis) + (Cardiac/Resp Disease & ↑Thyroid Acropathy)
- Perfusion + CRT
-
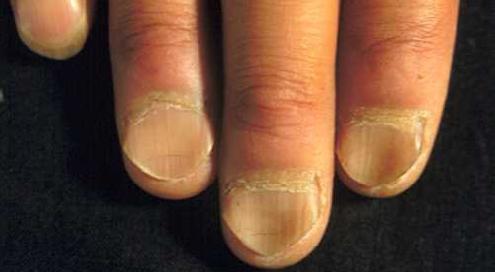
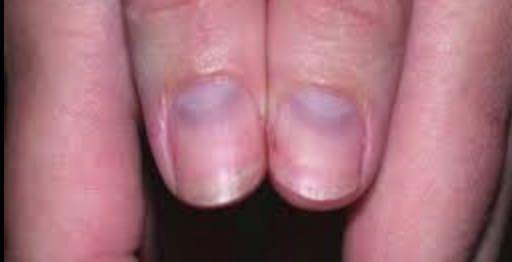
- Leukonychia & Muercke’s Lines (Hypoalbuminaemia – Liver Failure, Nephrotic Syndrome)
- Koilonychia (Iron Deficiency – Blood Loss, GI Bleed, Malabsorption)
- Leukonychia & Muercke’s Lines (Hypoalbuminaemia – Liver Failure, Nephrotic Syndrome)
-
- Blue Lunulae (Wilson’s Copper Disease)
-
- Palmar Crease Pallor + Pale Nails (Anaemia)
- Palmar Erythema (↑Oestrogen in Liver Disease)
- Dupuytren’s Contracture (Alcoholic Hepatitis/Cirrhosis)
- Xanthomata (↑Cholesterol – Fatty Liver, Nephrotic Syndrome, Diabetes)
- Hepatic Flap (Asterixis – Hepatic Encephalopathy)
- Arms:
- Bruising, Petechiae
- Scratch Marks (Uraemic Pruritis)
- Uraemic Frost
- Acanthosis Nigricans in Axilla (GI Malignancy)
- Face:
- Eyes:
- Conjunctival Pallor (Anaemia)
- Scleral Icteris (Jaundice)
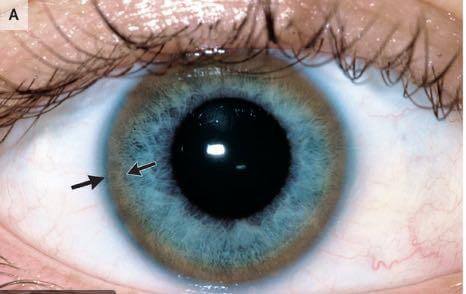
- Keyser Fleischer Rings (Wilson’s Disease)
- Eyes:
∙
-
-
- Iritis (Crohn’s/Ulcerative Colitis)
- Xanthelasma (↑Cholesterol – Biliary Obstruction, PBC, Cirrhosis, Diabetes)
- Mouth:
- Hydration
- Parotid Gland Enlargement (Alcoholism)
- Central/Peripheral Cyanosis
- Mucosal Ulcers (Crohn’s/UC)
- Glossitis/Angular Stomatitis (Anaemia, Alcoholism B12, Malabsorption B12)
-
∙
-
-
- Peutz Jegher’s Pigmentation
- Fetor Hepaticus
- Mucosal Petechiae
- Leukoplakia (Spirits, Smoking, Sepsis, Syphilis, Shit teeth)
-
∙
- Neck:
- Supraclavicular Lymph Nodes (Virchow’s Node = GI/Lung Malignancy)
- Chest:
- Gynaecomastia (↑Oestrogen – Liver Failure)
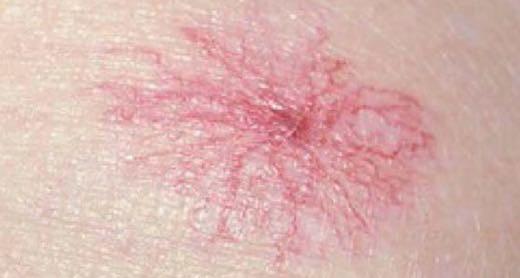
- >3 Spider Naevi (↑Oestrogen – Liver Failure)
- Abdomen:
- Inspection:
- Abdominal Distension (Ascites, Obstruction)
- Scars
- Visible Masses (Cancer, Hernias)
- Visible Peristalsis (Obstruction)
- Bruising, Petechiae (Liver Failure)
- Cullen’s & Grey Turner’s Sign (Pancreatitis, Haemoperitoneum)
- Caput Medusa (Portal HTN, Cirrhosis)
- Striae
- Vesicles (Shingles)
- Palpation:
- Light Palpation – Tenderness, Guarding, Rigidity, Rebound? (Peritonitis)
- Deep Palpation – Masses?
- Hepatomegaly (Fatty Liver, Portal HTN, Hepatitis, Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Polycystic Liver)
- Small Liver (Cirrhosis)
- Pulsatile Liver (Tricuspid Regurg)
- Splenomegaly (Infection, Haem.Malignancy)
- Ballott Kidneys
- Aortic Aneurysm
- Para-Aortic Lymph Nodes (Malignancy, Infection)
- Special Tests:
- Cholecystitis: Murphey’s Sign
- Appendicitis: Rovsing’s Sign, Pain @ Mcburney’s Point, Psoas Sign, Obturator Sign.
- Pyelonephritis/Renal Stones: Murphey’s Kidney Punch
- Percussion:
- Ascites & Shifting Dullness (Portal HTN, Liver Failure, Renal Failure) + (Heart Failure)
- Percuss for Splenomegaly & Hepatomegaly
- Ascites & Shifting Dullness (Portal HTN, Liver Failure, Renal Failure) + (Heart Failure)
- Auscultation:
- Bowel Sounds (Absent in Ileus)
- Renal Bruits
- + Deferred PR Exam for Cancer, Blood, Malena.
- Inspection:
- Legs:
- Pitting Oedema (Liver Failure, Renal Failure)
- Bruising, Petechiae (Liver Failure)
- Varicosities (Portal Hypertension)
- Feet:
- Perfusion & CRT
- Xanthomata (↑Cholesterol – Biliary Obstruction, PBC, Cholelithiasis)
- Leukonychia & Muercke’s Lines (Hypoalbuminaemia – Liver Failure, Nephrotic Syndrome)
- Clubbing (Crohn’s Disease & Ulcerative Colitis)
GI related disorders and Clinical Co-relation:
Mallory Weiss Syndrome Tear: = Oesophageal laceration – (Longitudianl tear)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Dysphagia & Odynophagia
- Chest Pain
- Haematemesis
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Normal (Tachy if Pain/Dehydration/Blood Loss), Bradypnoeic (if Alkalotic from Vomiting)
- Signs of Causes:
- Obesity (Gluttony), Subconjunctival Haemorrhages (Severe Coughing), Low BMI (Bulimia), Destroyed dentition (Bulimia)
- NB: Nothing to do with Alcohol.
- Vitals:
Oesophageal Varices (Due to Portal Hypertension): (Often 2o to alcoholic cirrhosis)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Hematemesis
- Hematochezia
- May Rupture ➔ Massive Bleeding
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Normal unless Haemorrhage (Tachycardia, Tachypnoea, Hypotension)
- Other:
- Portal HTN (Caput Medusa, Ascites, Hepatomegaly, Splenomegaly, Pedal Oedema)
- If Cirrhosis (Palmar Erythema, Mee’s/Meurkhe’s/Leukonychia, Jaundice, Xanthomata, Xanthelasma, Scleral Icteris, Hepatic Fetor, Hepatic Flap, Ascites, Pedal Oedema)
- Signs of Causes:
- Chronic Alcoholism (Dupuytren’s Contracture, Cerebellar Dysfunction)
- Vitals:
Gastritis: = Inflammation of the Stomach Lining
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Epigastric Pain
- Nausea/Vomiting
- Indigestion (Dyspepsia)
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Tachycardia (if infection), all else normal
- Other:
- Epigastric Tenderness
- Signs of Causes:
- Infection
- Pernicious Anaemia (B12 Deficiency ➔ Peripheral Neuropathy & Macro.Anaemia)
- Alcohol Abuse (Dupuytren’s Contracture, Macro.Anaemia, Cerebellar Dysfunction)
- Vitals:
Peptic Ulcer Disease: (NSAIDs, H.Pylori, or Gastrinoma/ZE-Synd)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Burning Epigastric Pain (Relieved by Food)
- Haematemesis/Melena
- Nausea & Vomiting
- (If Perforated ➔ Acute Peritonitis & Shock)
- (If Pyloric Stenosis ➔ Irretractable Vomiting)
- NB: May ➔ Gastric Ca. ➔ Weight Loss
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Normal unless Perforated (Tachycardia, Tachypnoea, Hypotension)
- If Anaemic from GI Bleeding (Tachycardia, Tachypnoea)
- Other:
- But may have weight-loss
- If Anaemic from NSAIDs ➔ Pale Nails, Koilonychia (↓Fe), Palmar Pallor, SC Pallor, Atrophic Glossitis.
- If Ruptured ➔ Peritonism (Guarding, Rigidity, Rebound, Shoulder-tip Pain, Shallow Breathing, Cullen’s Sign, Grey Turner’s Sign, Peripheral Shutdown, ALOC)
- Vitals:
Gastric & Duodenal Cancers: (“Fungating” – H.Pylori) (“Leather Bottle” – Familial) 
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Asymptomatic until Advanced Disease
- Early Symptoms: Epigastric Pain, Nausea/Vomiting, Anorexia/Weight Loss, Adenopathy, Anaemia.
- Late Symptoms: Malignant Ascites/Jaundice, Symptoms of Brain/Bone/Lung Mets
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Fever, Tachycardia (If Anaemia or Hypovolaemic), Tachypnoea (If Anaemia)
- Other:
- Virchow’s Node (L-Supraclavicular LN), Acanthosis Nigricans in Axillae,
- Anaemia (Pale Nails, Palmar Pallor, SC Pallor, Atrophic Glossitis)
- Metastases (Oesophagus, LN, Liver, Lungs)
- Signs of Causes:
- Peutz Jegher’s Syndrome (Mouth Pigmentation, Clubbing)
- Alcoholism, Smoking
- Vitals:
Coeliac Disease: (SI Gluten Hypersensitivity)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Can Present at ANY Age (Peaks = Infancy, in 50’s)
- Fatigue, Malaise
- Diarrhoea/Steatorrhoea
- Abdo Pain/Discomfort/Bloating
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Normal
- Other:
- Weight Loss, Mouth Ulcers, Angular Stomatitis, Atrophic Glossitis,
- Vitals:
Radiation Enteritis: (Fibrosis from Radiotherapy)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Acute Sx – Nausea, Vomiting, Diarrhoea, Abdo Pain. (Improves within 6wks of Radiation)
- Chronic Sx – (Symptoms for >3mths) Pain due to Obstruction, Malabsorption, Diarrhoea, Tenesmus
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Tachycardia (Hypovolaemia/Anaemia), Tachypnoea (Anaemia), Hypotension (Hypovolaemia)
- Other:
- Radiation Tattoos, Radiation Fibrosis of Skin (Abdomen/Back/Perineum), Anal Fissures (Diarrhoea), Surgical Scars, Abdominal Distension
- Vitals:
Whipples Disease: (Chronic Bacterial Infection: Tropheryma Whipplei)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Initially – Arthritis & Arthralgia
- YEARS Later ➔Fever, Abdo Pain, Diarrhoea, Weight Loss ➔ MALABSORPTION
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Fever, Tachycardia
- Other:
- Lymphadenopathy, Poly Arthritis, Steatorrhoea, Oedema, Anaemia (Fe/B12), Weight Loss
- Can ➔ Brain Damage (Mental Changes/Memory Loss)
- Can ➔ Endocarditis (Heart Murmur)
- Vitals:
Acute Bacterial Diarrhoeal Diseases:
(ETE.Coli = Traveller’s)
(S.aureus & Salmonella = Food Poisoning) (Shigella = Dysentery)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Hyperacute (<24hrs) – Probably ETEC Toxin
- Sub-Acute (<3-5days) – Probably Infective Gastroenteritis (Food Poisoning)
- (If Chronic, more likely to be Parasitic than Bacterial)
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Fever, Tachycardia, Tachypnoea, Hypotension (Hypovolaemic)
- Other:
- Peripheral Shutdown, ↑CRT, Low-Volume Tachycardia, Dry Mucosae, Enophthalmos, Loss of Skin Turgor)
- Signs of Causes:
- Dysentery (Blood & Pus in Stools) = Shigella
- Vitals:
Acute Viral Diarrhoea:
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Vomiting
- + Watery Diarrhoea
- + Fever
- (Typically In a Child/Infant)
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
-
- Vitals:
- Fever, Tachycardia, Tachypnoea, Hypotension (Hypovolaemic)
- Other:
- Typically In a Child/Infant ➔ Irritability, Poor Feeding
- Peripheral Shutdown, ↑CRT, Low-Volume Tachycardia, Dry Mucosae, Enophthalmos, Loss of Skin Turgor)
- Signs of Causes:
- Hippie Mother Not Vaccinating!
- Vitals:
-
Chronic Diarrhoea (Usually Parasitic/ Irritable Bowel/ or Malignancy)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Long-Term Diarrhoea
- Weight Loss
- Fatigue
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Normal
- Other:
- Anaemia (Microbleeding ➔ Pale Nails, Koilonychia, Palmar Pallor, SC Pallor, Atrophic Glossitis), Anal Fissures.
- If CD/UC – Clubbing, Mucosal Ulcers, Red Eyes
- Signs of Causes:
- Immunocompromise
- (Also Think Coeliac Disease & Colon Ca)
- Vitals:
Intestinal Tuberculosis
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- **Fever + Night Sweats
- **Weight Loss
- *Ileocaecal Area is most commonly affected ➔ RIF Abdominal Pain
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Fever, Tachycardia, Tachypnoea (if Pulmonary TB)
- Other:
- Palpable Masses, Generalised Peritonitis, Bowel Obstruction, Anaemia
- Signs of Causes:
- Immunocompromised (HIV/Drugs)
- Pulmonary TB
- Vitals:
Appendicitis:
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Initially Umbilical Pain ➔ Severe RIGHT Iliac Fossa Pain
- Fever
- Nausea/Vomiting/Anorexia/Diarrhoea(occasionally)
- (Ie. Similar to Diverticulitis, but on the Right)
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Fever, Tachycardia,
- Other:
- R-Iliac Fossa Pain/Tenderness/Guarding
- Rovsing’s Sign: Referred Rebound Pain in the RIF when the LIF is Pressed.
- Psoas Sign: RIF Pain on Flexion of the Hip
- Obturator Sign: RIF Pain on Internal Rotation of the Hip
- Mcburney’s Sign: Deep tenderness at McBurney’s point
- If Ruptured Appendix:
- Sepsis, Shock, High Fever, Generalised Peritonitis (Guarding/Rigidity/Rebound)
- Vitals:
Pseudomembranous Colitis:
Clostridium Difficile Overgrowth due to Antibiotic ➔ ↓Gut Flora (C.Diff is Directly Cytotoxic)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Onset within 2days of Antibiotics; Persists for 2wks After.
- Fever,
- Abdo Cramps
- Profuse Water Diarrhoea (<10/day)
- Faecal Urgency
- NB: Can Perforate
- NB: Can ➔ Toxic Megacolon
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Fever, Tachycardia (Infection & Dehydration), Tachypnoea (infection), Hypotension (Dehydration)
- Other:
- Abdo Pain, Haematochezia
- (If Perforation – Peritonitis, Shoulder-tip Pain, Cullen’s/Grey-Turner’s, Shock)
- (If Toxic Megacolon – Abdominal Distension, Abdo Tenderness, Septic Shock, Loss of Bowel Sounds)
- Signs of Causes:
- History of Antibiotic Usage
- Vitals:
Diverticulosis/Diverticulitis:
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- NB: Diverticulosis is Asymptomatic
- NB: Diverticul-ITIS is Symptomatic:
- Severe LEFT Iliac Fossa Pain
- Fever
- Constipation
- (IE. Similar to Appendicitis, but on the Left)
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Fever, Tachycardia,
- Other:
- LIF Tenderness/Guarding/Rigidity
- GI Bleeding ➔ Anaemia (Pale Nails, Koilonychia, Palmar/SC Pallor, Glossitis)
- (NB: If Perforation ➔ Peritionitis, Shoulder-Tip Pain, Sepsis, Shock, Death)
- Signs of Causes:
- Opioid Addicts (Chronic Constipation), Paraplegic, Multiparity.
- Vitals:
Crohn’s Disease: (Mouth ➔ Anus)(Patchy)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Typically Starts @ Ileocecal Valve (RIF)
- Common Symptoms (Both CD & UC):
- **Abdominal Pain/Severe Internal Cramps
- **Vomiting/Diarrhoea *(Porridge-like, Fatty)
- **Rectal Bleeding
- (+ Fever, Weight Loss)
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Fever,
- Other:
- Clubbing
- Mouth Ulcers & Anus Involvement,
- GI Bleeding ➔ Anaemia (Pale Nails, Koilonychia, Palmar/SC Pallor, Glossitis)
- Signs of Causes:
- Autoimmune (Arthritis, Iritis, Pyoderma Gangrenosum, Primary Biliary Cirrhosis)
- Vitals:
Ulcerative Colitis: (Typically affects Colon)(Continuous)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Typically Starts @ Rectum (LIF)
- Common Symptoms (Both CD & UC):
- **Abdominal Pain/Severe Internal Cramps
- **Vomiting/Diarrhoea *(Bloody & Mucus – but NO Pus. {Not Dysentery])
- **Rectal Bleeding
- (+ Tenesmus)
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Afebrile,
- Other:
- Clubbing
- No Mouth or Anus Involvement,
- GI Bleeding ➔ Anaemia (Pale Nails, Koilonychia, Palmar/SC Pallor, Glossitis)
- Signs of Causes:
- Autoimmune (Arthritis, Iritis, Pyoderma Gangrenosum, Primary Biliary Cirrhosis)
- Vitals:
Irritable Bowel Syndrome/‘Spastic Colon’:
(Umbrella Term)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Chronic Abdo Pain/Discomfort
- Alternating Bowel Habits (+ Tenesmus)
- (All Investigations Normal)
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Normal
- Other:
- Normal
- Signs of Causes:
- *Stress/Anxiety/Depression, Chronic Pain, Gut Hypersensitivity.
- Vitals:
Hirschsprung’s Disease (“Congenital Aganglionic Megacolon”):
(Immotile Section of Colon)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Presentation within 2-3days after Birth:
- Delayed Meconium (First Defecation)
- Abdo Distension
- Vomiting
- Presentation within 2-3days after Birth:
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Normal
- Other:
- Abdominal Distension & Tenderness, Poor Feeding, Irritability, Anorexia
- Signs of Causes:
- Baby
- Vitals:
Meckel’s Diverticulum: (Congenital SI True Diverticulum)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- (NB: Majority are Asymptomatic)
- Presentation @ 2yrs Old:
- Malena (Bleeding)
- Severe Central Abdo Pain (Obstruction/Volvulus/Intussusception)
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Tachycardia (Pain/if infected), Tachypnoea (Pain), Hypertension (Pain)
- Other:
- Abdominal Distension, Abdominal Tenderness, Peritonitis & Sepsis (perforation), Loss of Bowel Sounds, Visible Peristalsis, Cullens/Grey-Turners (Hemoperitoneum)
- Signs of Causes: Baby
- Vitals:
Colonic Polyps: (NB: Common in Autosomal Dominant Peutz-Jeger’s Syndrome)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Asymptomatic in Early Stages
- (+/- Change in Bowel Habits)
- (+/- Syx of Anaemia)
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Normal
- Other:
- None
- If Anaemia (Koilonychia, Pale Nails, PC/SC Pallor, Atrophic Glossitis)
- Signs of Causes:
- Peutz-Jeger’s Syndrome (Clubbing + Melanin Pigmentation on Lips & Hands)
- Vitals:
Bowel Cancer (Sporadic & Inherited):
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Bowel Ca. Common Symptoms:
- (Asymptomatic in Early Stages)
- Change in Bowel Habit & Stool Shape
- Blood Mixed Within Stool (+/- Anaemia)
- Abdominal Cramping & Bloating
- Fevers/Night Sweats
- Weight Loss
- Fatigue
- (Late ➔ Bowel Obstruction +/- Metastasis)
- HNPCC; Amsterdam Criteria:
- 1. Must have 3 Affected Relatives
- 2. >One Relatives must be a 1st-Degree
- 3. FamHx must span >2 Generations
- 4. 1+ cases diagnosed @ <50yrs.
- FAP:
- APC Gene Mutation
- Bowel Ca. Common Symptoms:
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Tachycardia (if Anaemia/Hypovolaemic/Perforation/Septic)
- Tachypnoea (if Anaemia/Perforation/Septic)
- Hypotension (If Perforation/Septic/Shock)
- Febrile (If Septic)
- Other:
- Acanthosis Nigricans in Axillae (Sign of GI Malignancy)
- If Anaemia (Koilonychia, Pale Nails, PC/SC Pallor, Atrophic Glossitis)
- If Shock (↑CRT, Cool Peripheries, Peripheral Cyanosis, Low-Vol Pulse, Dry Mucosae)
- If Perf/Peritonism (Cullen’s/Grey-Turner’s Signs, Tenderness/Guarding/Rebound, Rigidity, Shoulder-Tip Pain)
- If Metastasis to Liver (Obstructive Jaundice, Clubbing, Leukonychia, Muercke’s Lines, Mee’s Lines, Xanthomata, Palmar Erythema, Scleral Icteris, Hepatic Flap, Hepatic Encephalopathy, Xanthelasma, Hepatic Fetor, Hepatomegaly, Gynaecomastia, Spider Naevi, Abdominal Distension, Caput Medusa, Ascites, Pedal oedema, Bruising, Scratchmarks)
- Vitals:
-
- Signs of Causes:
- NB: Both HNPCC & FAP ➔ ↑Risk of other Cancers (Endometrial/Gastric/Ovarian)
- Signs of Causes:
Carcinoid Tumour of the Intestines:
(Serotonin Neuroendocrine Tumour)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Hot Flushes
- Watery Diarrhoea
- Abdominal Pain
- Palpitations
- (3 Common Sites = Appendix, Terminal Ileum, Rectum; Also the R-Sided Heart Valves)
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Hypotension (Systemic Vasodilation; & Hypovolaemia), Tachycardia (Hypovol)
- Other:
- Cardiac Abnormalities – Pulmonary Stenosis or Tricuspid Regurgitation ➔ Tender Pulsatile Hepatomegaly.
- “Pellagra” (Sign of Niacin/B3 Deficiency) ➔ Delusions, Confusion, Scaly Skin Sores.
- Vitals:
Fulminant Hepatic Failure (Acute Liver Failure):
(Alcohol/Drugs/Chronic Hepatitis/Biliary Obstruction/Etc)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Jaundice, Pruritis
- Bleeding, Bruising
- RUQ Pain
- Fetor Hepaticus
- Cerebral Oedema, Vomiting
- Hepatic Encephalopathy (within 2 wks)
- Death without transplant.
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- May be Febrile
- Other:
- Jaundice, Scratch marks,
- Bruising/Petechiae/Purpura,
- Hepatic Flap, Hepatic Encephalopathy, Hepatic Fetor
- RUQ Tenderness
- Oedema
- Vitals:
Alcoholic Liver Disease (Alcoholic Hepatitis):
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Jaundice
- RUQ Tenderness
- Palpitations
- Gynaecomastia, Spider Naevi, Testicular Atrophy
- Abdo Distension
- (Ataxia)
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- AF (If Dilated Cardiomyopathy)
- Other:
- Fatty Liver Changes ➔ Hepatomegaly, RUQ Tenderness
- If Portal Hypertension ➔ Hepatomegaly, Splenomegaly, Ascites, Pedal Oedema
- CLD (Clubbing, Leukonychia, Muercke’s Lines, Mee’s Lines, Xanthomata, Palmar Erythema, Bruising, Scratchmarks, Scleral Icteris, Hepatic Flap, Hepatic Encephalopathy, Xanthelasma, Hepatic Fetor, Hepatomegaly, Gynaecomastia, Spider Naevi, Abdominal Distension, Caput Medusa, Testicular Atrophy, Ascites, Pedal oedema)
- Signs of Causes:
- Dupuytren’s Contracture
- **↓Thiamine ➔Wernicke/Korsakoff Syndrome, Cerebellar Degeneration, Peripheral Neuropathy
- Dilated Cardiomyopathy
- Pancreatitis
- Anaemia (Macrocytic – B12 Deficiency) (Microcytic – if GI Blood Loss)
- Vitals:
Hepatic Cirrhosis (Chronic Liver Failure):
(Alcohol/Drugs/Chronic Hepatitis/Biliary Obstruction/Haemochromatosis/ Wilson’s Disease/Etc)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- May be Asymptomatic
- RUQ Pain
- Pruritis (Jaundice), Bruising (Liver Failure)
- Abdominal Distension, Ankle Swelling, Caput Medusa (Portal Hypertension)
- Gynaecomastia, ↓Libido, Amenorrhoea, Palmar Erythema, Spider Naevi (Oestrogen Excess)
- Confusion/Forgetfulness/Drowsiness/Flap/ Coma/Seizures (Hepatic Encephalopathy)
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Normal
- Other:
- Jaundice, Ascites, Pedal Oedema
- Clubbing, Leukonychia, Muercke’s Lines, Mee’s Lines, Xanthomata, Palmar Erythema, Bruising, Scratchmarks, Scleral Icteris, Hepatic Flap, Hepatic Encephalopathy, Xanthelasma, Hepatic Fetor, Shrunken Nodular Liver (Micro or Macro-Nodular depending on Aetiology), Splenomegaly, Gynaecomastia, Spider Naevi, Abdominal Distension, Caput Medusa, Testicular Atrophy, Ascites, Pedal oedema)
- Signs of Causes:
- IVDU, Alcoholism, Tattoos, Skin Pigmentation (Haemochromatosis), Cachexia (Ca), Xanthelasma/mata (Chronic Biliary Obstruction)
- Vitals:
Hepatitis-Viruses ➔ Acute Hepatitis:
(Hep A & E)(Faecal-Oral)(Acute ONLY)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Epidemics Common
- Acute Hepatitis ONLY:
- Viraemia ➔ Flu-like Symptoms (Fever, Malaise, Anorexia, Nausea, Arthralgia)
- Jaundice after 10days
- (**NB: 20% Mortality of Hep.E in Pregnancy)
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Fever, Tachycardia
- Other:
- Jaundice (Intrahepatic Cholestasis :. Pale Stools & Dark Urine)
- +/- Hepatomegaly
- +/- Splenomegaly
- +/- Tender Lymphadenopathy
- Vitals:
Hepatitis-Viruses ➔ Chronic Hepatitis:
(Hep B, B+D, & C)(Blood-Transmission)(Acute➔Chronic)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Acute ➔ Non-Specific Viral Symptoms:
- Viraemia ➔ Flu-like Symptoms (Fever, Malaise, Anorexia, Nausea, Arthralgia)
- (90% of Hep B ➔ Full Recovery)
- (10% of Hep C ➔ Full Recovery)
- Chronic ➔ Chronic Hepatitis Symptoms:
- May have Non-Specific Viral Syx if Reactivation (Eg. “Chronic Active Hep B”)
- OR…May be Completely Asymptomatic until Cirrhosis ➔ Liver Failure
- Cirrhosis ➔ Liver Failure:
- Abdominal Distension +Ankle Swelling
- Pruritis (Jaundice), Bruising
- Gynaecomastia, ↓Libido, Amenorrhoea (Oestrogen Excess)
- Confusion/Drowsiness/Coma/Flap (Hepatic Encephalopathy)
- Acute ➔ Non-Specific Viral Symptoms:
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
Acute:
-
- Vitals:
- Fever, Tachycardia
- Other:
- Jaundice (Intrahepatic Cholestasis :. Pale Stools & Dark Urine)
- +/- Hepatomegaly, +/- Splenomegaly, +/- Tender Lymphadenopathy
- Vitals:
Chronic:
-
- Vitals:
- (If Active ➔ Fever, Tachycardia)
- If Subclinical ➔ Normal Vitals.
- Other:
- Jaundice (Both Types),
- Small, Nodular Liver
- Signs of Portal HTN – (Telangiectasias, Caput Medusa, Ascites, Pedal Oedema, Hepatomegaly, Splenomegaly, Gynaecomastia)
- Hep. Encephalopathy
- Vitals:
(10% of Hep B & 90% of Hep C) ➔ Cirrhosis ➔ Liver Failure:
-
- Signs:
- Clubbing, Leukonychia, Muercke’s Lines, Mee’s Lines, Xanthomata, Palmar Erythema, Bruising, Scratchmarks, Scleral Icteris, Hepatic Flap, Hepatic Encephalopathy, Xanthelasma, Hepatic Fetor, Gynaecomastia, Spider Naevi, Abdominal Distension, Caput Medusa, Testicular Atrophy, Ascites, Pedal oedema.
- Signs:
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis (AKA: “Chronic, Non-Suppurative Destructive Cholangitis”):
(Genetic Autoimmune)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Mid-Aged Females
- Insidious Onset
- Pruritis, then (Cholestatic) Jaundice
- Fatigue
- Hepatomegaly
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Normal
- Other:
- Jaundice, Ascites, Pedal Oedema
- Clubbing, Leukonychia, Muercke’s Lines, Mee’s Lines, Xanthomata, Palmar Erythema, Bruising, Scratchmarks, Scleral Icteris, Hepatic Flap, Hepatic Encephalopathy, Xanthelasma, Hepatic Fetor, Shrunken Nodular Liver (Micro or Macro-Nodular depending on Aetiology), Splenomegaly, Gynaecomastia, Spider Naevi, Abdominal Distension, Caput Medusa, Testicular Atrophy, Ascites, Pedal oedema)
- Signs of Causes:
- Commonly Mid-Age Female.
- Vitals:
Gilbert’s Syndrome:(Genetic; Benign)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Asymptomatic
- Occasional Mild Jaundice (Associated with Fasting/Infection /Stress/Exertion).
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Normal
- Other:
- Occasional Jaundice Precipitated by Stress/Infection/Exertion/etc.
- Signs of Causes:
- Jaundice + Young + Family Hx of Jaundice
- Vitals:
Haemochromatosis – (Primary – Genetic; or Secondary)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Initially Asymptomatic
- Early – (Fatigue, Arthralgia, Loss of Libido)
- Later – (Skin Bronzing, Abdo Pain, Hepatomegaly, Liver Cirrhosis)
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Skin “Bronzing”
- Cirrhosis – (Jaundice, Bruising, Ascites, Oedema, etc.)
- Other Complications:
- Heart – Cardiomyopathy
- Endocrine Glands – Failure of gland:
- Joints – Arthritis (Iron Deposition in the Joints)
- Signs of Causes:
- (Acquired – Transfusions/Supplements/Haemolysis)
Liver Abscesses:(Infection – Typically E.Coli – 2o to Sepsis)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Fever, Rigors, Malaise,
- Anorexia, Weight Loss
- Vomiting, Abdo Pain
- (Similar to TB)
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Fever, Tachycardia, Tachypnoea, Hypotension (if Septic Shock)
- Other:
- Sepsis, Jaundiced,
- Tender, Enlarged Liver
- Signs of Causes:
- Intra-Abdominal Sepsis
- Vitals:
Hepatocellular Carcinoma:(Primary Liver Tumour)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- (NB: EXTREME RISK in Chronic Carriers of HBV, HCV)
- (NB: EXTREME RISK in Cirrhotics)
- RUQ Pain
- Fever, Anorexia, Weight Loss
- Ascites
- NB: Suspect HCC if you see these signs in a Cirrhotic.
- (NB: ↑Serum a-Fetoprotein)
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Fever
- Other:
- RUQ Tenderness/Mass, Hepatomegaly,
- Anorexia/Weight Loss
- Ascites/Peripheral Oedema
- (+/- Obstructive Jaundice)
- Signs of Causes:
- Cirrhosis (Shrunken, Nodular Liver + Signs of Chronic Liver Failure)
- HBV/HCV Infected (IVDU/Homosexual/Tattoos/Prostitutes/etc)
- Vitals:
Liver Metastases: (Secondary Liver Ca’s)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- RUQ Pain
- Jaundice (if Obstructive)
- Fever, Anorexia, Weight Loss
- + Previous Hx of Cancer
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Fever
- Other:
- RUQ Pain
- Fevers/Sweats
- Confusion
- Jaundice
- (**Will eventually progress to show signs of Chronic Liver Failure)
- Signs of Causes:
- Typically from Colorectal Ca, Breast Ca, Lung Ca, Melanoma.
- Vitals:
Biliary Colic: (AKA: “Cholelithiasis”)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- NB: Cholelithiasis is typically Asymptomatic.
- HOWEVER if Gallstones get Stuck ➔ Biliary Colic:
- ( = Biliary Pain for <3hrs)
- Severe, Colicky RUQ Pain
- Radiation to the R-Shoulder
- Fat Intolerance ➔ Clay Stools
- (NB: Can ➔ Perforation or Obstructive Pancreatitis)
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Pain ➔ Tachycardia, Tachypnoea, Hypertension
- Other:
- Positive Murphey’s Sign (RUQ pain in deep inspiration)
- Obstructive Jaundice (Pale Stools, Dark Urine)
- Signs of Causes:
- Xanthelasma/Xanthomata (Hypercholesterolaemia), Pregnancy, Obesity, Rapid Weight LOSS, Cystic Fibrosis
- Vitals:
Acute Cholecystitis:
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- ( = Biliary Pain for >3hrs)
- Severe, Colicky RUQ Pain
- Radiation to the R-Shoulder
- *Pain Associated/Exacerbated with FOOD
- *Nausea, Vomiting
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Fever, Tachycardia, Tachypnoea, Hypertension
- Other:
- Positive Murphey’s Sign (RUQ pain in deep inspiration)
- Obstructive Jaundice (Pale Stools, Dark Urine)
- Peritoneal Involvement – Rigidity/Guarding/Rebound
- RUQ Mass (Swollen Gallbladder)
- Signs of Causes:
- Xanthelasma/Xanthomata (Hypercholesterolaemia), Pregnancy, Obesity, Rapid Weight LOSS, Cystic Fibrosis
- Vitals:
Acute Pancreatitis:
(50% – Gallstones; 40% – Alcohol; 10% other)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Epigastric/Abdo Pain – Following Large Meal OR Alcohol
- Vomiting
- Shock
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Tachycardia (Shock), Hypotension (Shock), Tachypnoea (Shock)
- Other:
- Epigastric Tenderness,
- **Peritonitis ➔ Guarding, Rigidity, Rebound + Referred Shoulder Tip Pain
- If Haemorrhage ➔ (Cool Dry Peripheries, ↑CRT, Peripheral Cyanosis, Low-Vol Tachy, Dry Mucosae, Cullen’s & Grey-Turner’s Signs)
- Signs of Causes:
- Alcoholism (Ataxia, Anaemia, Dupuytren’s, Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome)
- Cholelithiasis (Xanthelasma, Xanthomata)
- Vitals:
Chronic Pancreatitis: **Alcohol Abuse
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Intermittent Epigastric Pain
- Weight Loss (Malabsorption)
- Steatorrhea
- ➔Secondary Diabetes
- (Can ➔ ➔ Pancreatic Cancer)
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- NA
- Other:
- Jaundice
- Weight Loss
- Epigastric Tenderness
- Signs of Causes:
- Alcoholism (Ataxia, Anaemia, Dupuytren’s, Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome)
- Vitals:
Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma:(Ductal Tumour):
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- NB: Asymptomatic until Advanced Diasease
- Pain – Mid Epigastrium ➔ Back
- Migratory Venous Thrombosis (Trousseau Sign)
- **Anorexia & Weight Loss
- **Extreme Fatigue
- **Depression
- + Steatorrhoea, Malabsorption
- +/- Jaundice
- (NB: 25% 1yr Survival; 5% 5yr Survival)
- NB: Asymptomatic until Advanced Diasease
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
-
- Vitals:
- Fever
- Other:
- Obstructive Jaundice, Epigastric Pain (+/- Radiation to Back), Courvoisier’s Palpable Gallbladder,
- Low BMI, Migratory Venous Thrombosis (Trousseau Sign of Malignancy – Due to Hypercoaguability),
- 2o Diabetes
- Signs of Causes:
-
- Smoking, Alcohol, Chronic Pancreatitis (Eg. CF/Alcohol), Diabetes
- Familial Syndromes – Eg. BrCA, Peutz-Jeger’s Syndrome, Heriditary Pancreatitis
-
- Vitals:
-
Thank You so Much. Happy Learning!!