RENAL SYSTEM EXAMINATION NOTES
- Introduction, Wash Hands, Consent,
- Expose Patient & General Inspection:
- Alert & Orientated? (Uraemic Encephalopathy, UTI in Elderly)
- Acute pain or distress (Renal Colic, Pyelonephritis)
- Signs of Fluid Overload (Ascites, Peripheral Oedema)
- Signs of Dehydration (Causing Pre-Renal Failure)
- Facial Oedema (Nephrotic Syndrome)
- Obesity
- Scars
- In-Dwelling catheter
- Uraemic Fetor/Tinge (Ammonia Smell from Hyperuricaemia)
- Easy bruising on Arms, Legs & Trunk
- Vital Signs:
- Pulse:
- Tachycardia (If Infection, Hypovolaemia, Anaemia)
- Blood Pressure:
- Hypertension (Nephritic, Fluid Overload, Polycythaemia, Polycystic Kidney)
- Postural Hypotension (Anaemia, Hyponatraemia, Addisons, Diabetic Neuropathy)
- Respiratory Rate:
- Tachypnoea (if Renal Acidosis)
- Bradypnoea (if Renal Alkalosis)
- Temperature:
- Fever (Infection, Malignancy)
- Pulse:
- Hands:
- Peripheral Perfusion + CRT
- Mee’s Lines [single horizontal bands] (Arsenic/Heavy metal Poisoning)
- Muercke’s Lines [paired horizontal bands] & Leukonychia (Hypoalbuminaemia due to Nephrotic Syndrome)
- Palmar Crease Pallor & Pale Nails (Anaemia, Nephritic Syndrome)
- Palmar Crease Pigmentation (Addisons Disease ➔ Hyponatraemia & Hypovolaemia)
- Xanthomata (Diabetes, Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome)
- Gouty Tophi (Hyperuricaemia)
- Vasculitic Changes (Eg. Digital Infarcts – Sign of Autoimmune Glomerulonephritis)
- Arms:
- Uraemic Tinge/Uraemic Frost (Hyperuricaemia)
- Scratch Marks (Uraemia)
- AV-Fistulae (ESRD – Dialysis)
- Scars
- Asterixis (Uraemic Encephalopathy)
- Face:
- Butterfly Malar Rash of SLE (Cause of Renal Failure)
- Periorbital Oedema (Nephrotic Syndrome)
- Conjunctival Pallor (Anaemia, Nephritic Syndrome)
- Central/Peripheral Cyanosis
- Mouth Infections:
- (Strep Pharyngitis can ➔ PSGN Nephritic Syndrome)
- (Also Immunocompromise from Nephrotic Syndrome)
- Thrush (Immunocompromise from diabetes)
- Xanthelasma (Diabetes, Nephrotic Syndrome)
- Band Keratopathy (calcification of cornea due to 2o Hyperparathyroidism due to Vit D Deficiency)
- Dehydration (Nephrotic Syndrome)
- +Fundoscopy (Diabetic Retinopathy)
- Gum Hyperplasia (Methotrexate – Transplant Medication)
- Neck:
-
- Carotid Bruits (Hypercholesterolaemia, PVD, Diabetes)
- Vas Cath (Haemodialysis)
- Parathyroidectomy Scars (due to 2o Hyperparathyroidism due to VitD Deficiency)
- Acanthosis Nigricans (Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome, Obesity)
-
- Chest:
-
-
- CCF & Pulmonary Oedema (Due to Fluid Overload – Ie. Nephrotic Syndrome, CKD, ESRD)
-
-
- Abdomen:
-
-
- Inspection:
- Distension (Ascites in Nephrotic, Nephritic, Peritoneal Dialysis)
- Surgical Scars
- Peritoneal Dialysis Port
- Visible Masses
- Palpation:
- Renal masses (Polycystic Kidneys, Carcinoma)
- Insulin Injection Sites
- Polycystic Liver ➔Hepatomegaly (Polycystic Kidneys)
- Abdominal Aorta (Aneurysm ➔ Pre-Renal Failure)
- Enlarged Bladder (Obstructive Uropathy)
- Auscultation:
- Renal Bruits (Renal Artery Stenosis, Pre-Renal Failure)
- Bowel Sounds Present
- Percussion:
- Shifting Dullness (Ascites – Nephrotic, Nephritic, CKD)
- Inspection:
-
-
- Back:
-
-
- Surgical Scars
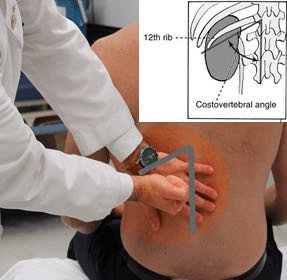
- Costovertebral Angle Tenderness (Murphey’s Kidney Punch) – (Pyelonephritis/Stones)
-
-
-
- Bony Tenderness
- Sacral Oedema
- Legs:
- Pitting Oedema (Nephrotic, Nephritic, CKD, Diabetes, PVD)
- Scratches/Uraemic Frost (Hyperuricaemia)
- Feet:
- Xanthomata (Hypercholesterolaemia)
- Gouty Tophi (Hyperuricaemia)
- Mee’s Lines (Arsenic/Heavy metal Poisoning)
- Meurkhe’s Lines & Leukonychia (Hypoalbuminaemia – Nephrotic Syndrome)
- Peripheral Perfusion + CRT
- Peripheral Pulses
- (+ Diabetic Neuropathy & Foot Examination)
- + Urine Dipstick
- Blood (Nephritic, Pyelonephritis, Renal Stones)
- Protein (Nephrotic, Nephritic)
- Signs of Intra-Renal Failure (Nephrotics & Nephritics):
- Nephrotic (Less Serious) (Autoimmune [adults] or Post-URTI [child]):
- Polyuria
- Massive Proteinuria ➔ Hypoalbuminaemia, Oedema & Periorbital Oedema
- Compensative Hyperlipidaemia (Xanthomata/Xanthelasma)
- Immunosuppression (Loss of IgG in Urine)
- Hypercoaguability (Loss of AT3 in Urine)
- No Haematuria
- Nephritic (More Serious) (Post URTI [Adults] or Post Strep-Pharyngitis [Children]):
- Anuria/Oliguria (↓GFR)
- Modest Proteinuria (NB: NORMAL ALBUMIN) ➔ Oedema
- Anaemia (PainLESS Haematuria)
- Hypertension
- Nephrotic (Less Serious) (Autoimmune [adults] or Post-URTI [child]):
Thank You so Much. Happy Learning!!