Table of Contents
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM EXAMINATION
- Introduction, Wash Hands, Consent
- General Inspection:
- Alert/Orientated
- Pain/Distress
- Body Habitus:
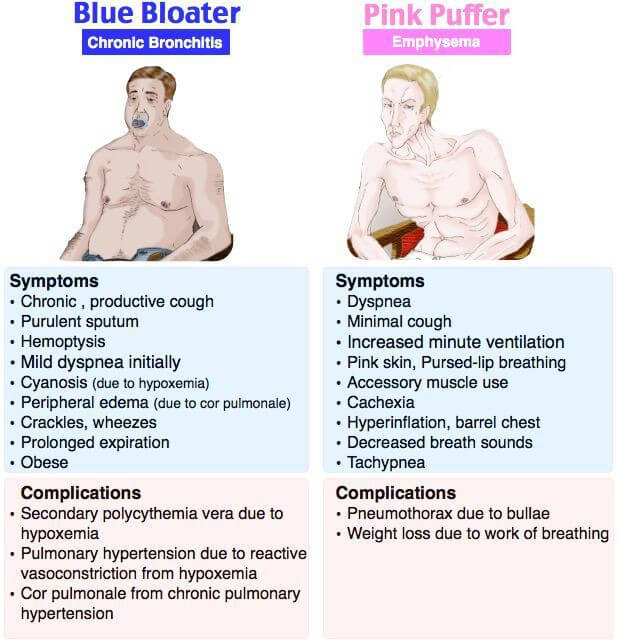
- Obesity (Blue Bloaters)
- Cachexia (Pink Puffers, Malignancy)
- Chest Deformities (Pectus Excavatum, Pectus Carinatum, Barrel Chest, Kyphosis, Lordosis)
- Chest Scars
- Respiratory Distress?
- Tripoding
- Pursed-Lip Breathing (Obstructive Lung Disease)
- Dyspnoea
- Audible Wheeze/Cough/Stridor (Obstructive Lung Disease)
- Intercostal Recession & Tracheal Tug (Restrictive Lung Disease)
- Colour:
- Cyanosis (Blue Bloaters)
- Plethora (Pink Puffers)
- Pallor (Anaemia)
- Vital Signs:
- Pulse:
- Tachycardia (Anaemia, Cyanosis, Infection)
- Blood Pressure:
- Typically Normal
- Postural Variation (Severe Anaemia)
- Pulsus Paradoxus (Severe COPD, Asthma, Tamponade, Pneumothorax)
- Respiratory Rate:
- Tachypnoeic (Anaemia & All Lung Diseases)
- SPO2:
- May be reduced or preserved (Must be recorded if the reading was on supplemental O2)
- Temperature:
- Fever (Infection)
- Pulse:
- Hands:
- Perfusion/CRT
- Clubbing (Chronic Cyanosis)
- Pale Nails (Anaemia)
- Koilonychia (Iron Deficiency Anaemia)
- Palmar Crease Pallor (Anaemia)
- Tar Staining (Smoking)
- Intrinsic Hand Muscle Wasting *(Pancoast Tumour)
- Hand Muscle Weakness *(Pancoast Tumour)
- Asterixis (CO2 Retention)
- Arms:
- HPOA (Lung Tumour)
- Pemberton’s Sign *(SVC Obstruction due to Pancoast Tumour)
- Face:
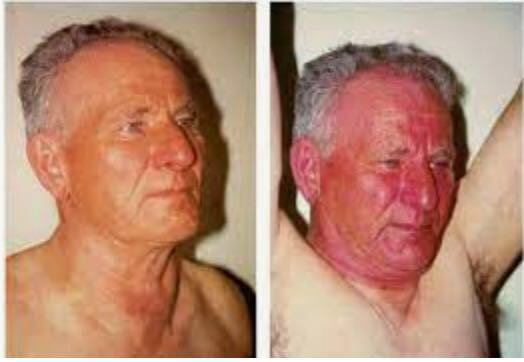
- Plethora (Polycythaemia, SVC Obstruction)
- Skin Lesions (SCC/BCCs)
- Conjunctival Pallor (Anaemia); Subconjunctival Haemorrhages (Severe Cough)
- Atrophic Glossitis/Angular Stomatitis (All Types of Anaemia)
- Hydration
- Central/Peripheral Cyanosis (All Lung Pathology)
- Leukoplakia/Erythroplakia (Premalignancy from Smoking)
- Tar-Stained Teeth (Smoking)
- HORNERS Syndrome (Sympathetic Nerve Palsy):
- Unilateral Ptosis, Anhydrosis, Miosis (Pinpoint Pupil, Enophthalmos, Laryngeal Hoarseness
- Neck:
- Virchow’s Node (Supraclavicular) (Malignancy)
- Cervical Lymphadenopathy (Infection, Malignancy)
- ↑JVP (SVC Obstruction – Pancoast Tumour)(or Pulmonary Hypertension)
- Abdojugular Reflux (Negative if SVC Obstruction)
- Tracheal Deviation (Atelectasis, Pneumothorax)
- Tracheal Tug (Restrictive Lung Disease)
- Chest – ONCE FROM BEHIND, ONCE FROM THE BACK:
- Inspection:
- Chest Deformities
- Scars
- Visualise Chest Expansion FROM BEHIND
- Palpation:
- Chest Expansion >5cm = Normal (From Behind)
- ↑Tactile Fremitis (Consolidation)
- Hoover’s Sign (Severe COPD, Emphysema, Asthma)
- Chest Wall Tenderness (Malignancy)
- Percussion:
- Dullness = Consolidation
- Stony Dullness = Pleural Effusion
- Hyperresonant = COPD/Emphysema/Asthma/Pneumothorax
- Lung Borders for Hyperinflation (6th rib anteriorly = normal) (COPD, Emphysema, Asthma)
- Auscultation:
- ↑Vocal Resonance
- Breath Sounds:
- Vesicular = Normal
- Bronchial = Consolidation
- Pleuritic Rub = Pleuritis/Mesothelioma
- Muffled = Pleural Effusion
- Inspiratory Crepitations/Crackles = Pulmonary Oedema/Pneumonia
- Expiratory Wheezes = Bronchial Disease
- (+ Mention Cardiovascular Examination)
- Inspection:
- Abdomen:
- Percuss & Palpate for Liver Ptosis (due to Lung Hyperinflation)
- Legs:
- Oedema
- Calf Tenderness & Erythema (DVT➔PE)
- Signs of Venous Stasis – Shiny Skin, Hair Loss, Venous Ulcers (DVT➔PE)
- Feet:
- Perfusion/CRT
- Clubbing
- Koilonychia (Iron Deficiency Anaemia)
- Pale Nails (Anaemia)
Respiratory Disorders and It’s Clinical Co-relation
Acute Bronchitis:
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Fever
- Productive, Wheezy Cough, +/- Dyspnoea
- + URTI Symptoms (Sore-Throat, Runny Nose, Sneezing, Hoarseness)
- + Non-Specific Viral (Fever, Malaise, Headache, Myalgia)
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Fever, Tachycardia, Tachypnoea
- Other:
- End-Expiratory Wheezes
- Signs of Causes:
- 2o to URTI
- Vitals:
Bronchial Asthma (Variable Obstructive):
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Asymptomatic unless during an “Attack”:
- Wheezy Dry Cough,
- Dyspnoea
- Anxiety
- If Severe:
- Exhaustion
- Inability to Speak in Full Sentences
- Asymptomatic unless during an “Attack”:
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Tachypnoea, Tachycardia,
- Other:
- Peripheral Cyanosis, Wheals, Hives, Rhinitis
- Accessory Muscle Usage
- Inspiratory Wheezes, Marked Expiratory Wheezes, Prolonged Expiratory Phase,
- ↑Chest Expansion (+/- Hyperinflated Lung Fields)
- Reduced Breath Sounds (Silent if Severe)
- NO signs of Consolidation (Normal ↑Fremitis, ↓Percussion & ↑Vocal Resonance)
- (+/- Pulsus Paradoxus if Severe)
- Signs of Causes:
- Signs of Atopia (Wheals, Allergic Rhinitis, Hives)
- Family History
- Vitals:
Bronchiectasis:
(Chronic Bronchial Thickening & Dilation + Mucus Accumulation due to ↓Mucociliary)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Wheezy Productive Cough
- Copious Purulent Sputum (Green/Yellow)
- (+/- Haemoptysis)
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Tachypnoea, Tachycardia, (+/- Fever if Infection)
- Other:
- Clubbing, Cyanosis, Cachexia,
- Foul-Smelling Sputum (Sometimes Haemoptysis)
- Coarse Pan-Inspiratory Crackles, End-Expiratory Wheezes
- (+/- Cor-Pulmonale if Severe)
- Signs of Causes:
- **Cystic Fibrosis (Clubbing, Peripheral Cyanosis, Sputum, Salty Frost, Wasting)
- Vitals:
Emphysema (Dry):
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Pink Puffers:
- Wheeze
- Severe Dyspnoea
- Weight Loss
- (+/- Peripheral Oedema & Ascites in Corpulmonale)
- Pink Puffers:
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Tachypnoea, Tachycardia
- Other:
- (NB: Does NOT cause Clubbing or Haemoptysis)
- Thin (No Oedema), Pink (No Cyanosis),
- Tachypnoea, Accessory Muscle Usage, Intercostal Recession, Tripoding (Stooping), Pursed- Lip Breathing, Barrel Chest,
- ↓Chest Expansion, Hoover’s Sign Positive, Tracheal Tug
- Hyperinflated Lungs Fields, Hyperresonant Percussion (Gas Trapping)
- ↓Breath Sounds, Early Expiratory Crackles (Small Airway Disease), (+/- Wheeze).
- (+/-↑JVP, Ascites, Oedema if RVF Due to Cor-Pulmonale)
- Signs of Causes:
- Heavy Smoking (Tar Staining, Smoke Smell, Yellow Teeth, Leuko/Erythroplakia)
- (If Young Age – Think Congenital a1-Antitrypsin Deficiency.)
- Vitals:
Chronic Bronchitis (Wet): (+/- Emphysema)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Blue Bloaters:
- Wet, Wheezy Productive Cough
- Chronic Sputum Production (>3mths/year for >2years)
- Severe Dyspnoea
- Oedema
- Blue Bloaters:
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Tachypnoea, Tachycardia
- Other:
- (NB: Does NOT cause Clubbing or Haemoptysis)
- Obese Patient, Gross Cyanosis (Central & Peripheral),
- Cor-Pulmonale (Ascites, Oedema, Cyanosis, ↑JVP)
- Tachypnoea, Accessory Muscle Usage, Intercostal Recession, Tripoding (Stooping), Pursed- Lip Breathing, Barrel Chest
- ↓Chest Expansion, Positive Hoover’s Sign, Tracheal Tug
- Hyperinflated Lung Fields, Hyperresonant Percussion
- ↓Breath Sounds, End-Expiratory Wheezes (Bronchial Disease)
- Signs of Causes:
- Heavy Smoking (Tar Staining, Smoke Smell, Yellow Teeth, Leuko/Erythroplakia)
- Vitals:
Pneumonia (Consolidation):
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Acute High Fever + Chills + Rigors
- Productive Cough (+/- Haemoptysis)
- Pleuritic Chest Pain
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Fever, Tachycardia, Tachypnoea
- Other:
- Appears Ill: P/C-Cyanosis, Exhaustion, Dyspnoeic, Respiratory Distress,
- Consolidation: Area of ↓Expansion, ↑Tactile Fremitis, Dull Percussion, Bronchial Breathing, ↑ Vocal Resonance.
- Bronchial Breath Sounds, Pleural Friction Rub, Pan-Inspiratory Crackles
- Signs of Causes:
-
- Broncho Pneumonia ➔ Diffuse, Patchy Consolidation
- Lobar Pneumonia ➔ Localised Consolidation
-
- Vitals:
Melioidosis: (Burkholderia Pseudomallei)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Presents Similar to TB but with Pneumonia:
- PUO (Fever, Night Sweats, Chills, Rigors)
- Skin Lesions (Abscesses/Ulcers)
- Pneumonia (Dyspnoea, Cough, Sputum, Pleuritic Chest Pain)
- (May ➔ Sepsis)
- Presents Similar to TB but with Pneumonia:
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Fever, Tachycardia, Tachypnoea
- Other:
- Cyanosis, Dyspnoea, Skin Lesions (Melioid Abscesses/Ulcers), Lymphadenopathy,
- Consolidation: Area of ↓Expansion, ↑Tactile Fremitis, Dull Percussion, Bronchial Breathing, ↑ Vocal Resonance.
- Bronchial Breath Sounds, Pleural Friction Rub, Pan-Inspiratory Crackles
- Signs of Causes:
-
- Living in Tropical NQ
-
- Vitals:
Pulmonary Tuberculosis:
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Fever, Night Sweats,
- Chronic Productive Cough (+/- Haemoptysis)
- Weight Loss
- +/- Pleuritic Chest Pain
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Fever, Tachycardia, Tachypnoea
- Other:
- Cachexia, Dyspnoea, Lymphadenopathy, Hepatomegaly, Splenomegaly,
- (NB: Cavitation Can ➔ Pleural Effusion (Stony Dullnes), Haemoptysis, Atelectasis)
- Signs of Causes:
- Immunocompromise (HIV), Immigrant, Overseas Travel,
- Vitals:
Pulmonary Embolism:
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Sudden, Severe Dyspnoea
- Pleuritic Chest Pain
- (+/- Haemoptysis)
- (+/- Syncope)
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Fever, Tachycardia, Tachypnoea, Hypotension (LVF)
- Other:
- RVF ➔ Cool Peripheries, ↑CRT, Peripheral Cyanosis, ↑JVP, RV-Heave, Tricuspid Regurg Murmur
- ↓Resp.Function ➔ Central Cyanosis
- Pleural Friction Rub,
- Signs of Causes:
- DVT – Calf Pain, Calf Tenderness, Calf Swelling/Erythema, Pedal Oedema.
- (B/G of Pregnancy, Air Travel, Recent Surgery, Clotting Disorders)
- Vitals:
Pulmonary Hypertension & Corpulmonale: (LVF, COPD)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- RVF Secondary to Pulmonary Hypertension:
- COPD: Dyspnoea, Cough, Wheeze
- Pul HTN: Cough/Dyspnoea/PND/Orthopnea
- RVF: Swelling (Legs, Abdo), Chest Pain
- RVF Secondary to Pulmonary Hypertension:
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Tachycardia (if LVF), Tachypnoea (if COPD/LVF), Hypotension (If LVF), Afebrile
- Other:
- If LVF: Cool Peripheries, ↑CRT, Peripheral & Central Cyanosis, Low Volume Pulse
- If COPD: Clubbing, Tar Staining, Peripheral & Central Cyanosis
- RVF: ↑JVP + a-Wave, RV-Heave, Medium Pan-Inspiratory Crackles in Lung Bases, Loud S2 (closure of Pul.Valve) Abdojugular Reflux Positive, Portal Hypertension (Tender Hepatomegaly), Ascites, Sacral/Pedal Oedema,
- Signs of Causes:
- LVF, Smoking, COPD, IPF
- Vitals:
Pneumothorax (Including Tension Px):
(Air in Pleural Space)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Similar Presentation to Pulmonary Embolism:
- Sudden, Severe Dyspnoea
- Pleuritic Chest Pain
- (+/- Syncope)
- Similar Presentation to Pulmonary Embolism:
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Tachycardia, Tachypnoea, Hypotension (Mediastinal Compression),
- Other:
- Cyanosis, Dyspnoea, Anxiety, Respiratory Distress,
- Peripheral Shutdown (↑CRT, Cool Pale Peripheries, Peripheral Cyanosis, Low-Vol Tachycardia)
- Tracheal Deviation AWAY from Affected Side (If Tension Ptx),
- @Site of Pneumothorax: ↓Chest Expansion, ↓Tactile Fremitis, Hyperresonant Percussion, Absent Breath Sounds, Absent Vocal Resonance.
- (IF KINKING OF GREAT VESSELS ➔ Syncope, Negative Abdojugular Reflux)
- Signs of Causes:
- Signs of Trauma, Signs of Smoking (Emphysema), Mechanical Ventilation,
- Vitals:
Atelectasis: (Collapsed Lung):
(Due to Airway Obstruction by Foreign Object or Cancer)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Dyspnoea
- Chest Pain
- (May Quickly ➔ Pneumonia)
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Tachypnoea
- Other:
- Dyspnoea,
- Tracheal Deviation TOWARDS the Affected Side.
- @Site of Atelectasis: ↓Chest Expansion, ↑Tactile Fremitis, Dull Percussion, Bronchial Breath Sounds, ↑Vocal Resonance
- Signs of Causes:
- Mucous (Asthma, Cystic Fibrosis), Foreign Body Aspiration, Bronchial Ca (Cachexia)
- Vitals:
Pleural Effusion:
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Sudden Severe Pleuritic Chest Pain (Worse on Inspiration)
- Dyspnoea
- Dry Cough
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Fever, Tachypnoea, Tachycardia,
- Other:
- Tracheal Deviation AWAY from Effusion
- Displaced Apex Beat AWAY from Effusion
- @ Site of Effusion: ↓Chest Expansion, ↓Tactile Fremitis, STONY DULLNESS, ↓Breath Sounds, ↓Vocal Resonance
- Signs of Causes:
- NB: ALWAYS Suspect Mesothelioma
- Portal Hypertension, Hypoalbuminaemia (CLD, Nephrotic Synd), Congestive L-Heart Failure, Lung Injury, Lung Infection.
- Vitals:
Interstitial Lung Diseases: (“Pneumoconioses”)
(Inhaled Dusts: Anthracosis, Asbestosis, Silicosis)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- (On a Background of Occupational Exposure)
- Chronic Cough (+/- Productive)
- Dyspnoea (+/- Cyanosis)
- (Asbestosis is most severe and can ➔Mesothelioma ➔ Pleural Effusions, Metastases)
- (On a Background of Occupational Exposure)
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Tachypnoea
- Other:
- Clubbing, Dyspnoea, Cyanosis, Cachexia, Accessory Muscle Usage, Intercostal Recession, Tracheal Tug.
- Cough
- ↓Chest Expansion,
- Fine Pan-Inspiratory Crackles
- + Restrictive Pulmonary Function Tests.
- Signs of Causes:
-
- Signs of Connective Tissue Diseases (Rheumatoid Arthritis, SLE, Scleroderma, Sjogren’s)
-
- Vitals:
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis:
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Gradual Onset of Symptoms
- Progressive Dyspnoea
- Dry Cough
- (Very Poor Prognosis – 3yrs – No Treatment)
- Gradual Onset of Symptoms
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Tachypnoea
- Other:
- Hypoxia/Cyanosis ➔ Clubbing
- Dry, Velcro-like inspiratory crackles
- Signs of Causes:
- Restrictive Pattern on Pulmonary Function Tests (↓VC, ↓TLC)
- Vitals:
Sarcoidosis: (Idiopathic Immune ➔ Non-Caseating Granulomas)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Systemic Disease – (Lungs, Eyes, Skin, LNs, Liver & Spleen)
- General: Fatigue, Weight Loss,
- Lungs: Dyspnoea, Dry Hacking Cough
- Eyes: Uveitis
- Skin: Erythema Nodosum (Nodules on Shins), Lupus Pernio (Red plaques), Hypertrophic Scars
- LNs: Lymphadenopathy
- Liver/Spleen: Organomegaly
- MSK: Arthralgia, Finger Swelling
- Heart: Heart Block, Syncope, Corpulmonale
- Systemic Disease – (Lungs, Eyes, Skin, LNs, Liver & Spleen)
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Tachypnoea
- Other:
- Dyspnoea, Cyanosis, Cachexia, Accessory Muscle Usage, Intercostal Recession, Tracheal Tug.
- Cough
- ↓Chest Expansion,
- Fine Pan-Inspiratory Crackles
- + Restrictive Pulmonary Function Tests.
- Vitals:
Wegener’s Granulomatosis: (Autoimmune)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Many Non-Specific Symptoms (Arthralgia, Myalgia, Night Sweats, Weight Loss, Red Eyes, URTI, Chronic Ear Infections, Fever)
- BUT Relevant as it can ➔ Pneumonia:
- Dyspnoea
- Cough (+/- Haemoptysis)
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Fever, Tachycardia, Tachypnoea,
- Other:
- Cachexia, Epistaxis, Nasal Sores, Various Skin Lesions, Haematuria, Conjunctivitis, Chest Pain, Cough (+/- Haemoptysis), Dyspnoea, Weakness, Wheezing.
- Vitals:
Mediastinal Compression: (Lung Ca, Lymphoma, Retrosternal Goitre, Aortic Aneurysm)
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Facial Plethora
- Supraclavicular Lymphadenopathy
- Hoarseness
- Horner’s Syndrome
- Dyspnoea
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Other:
- SVC Obstruction: Facial Cyanosis, Facial Plethora, Positive Pemberton’s, Periorbital Oedema, ↑Non-Pulsatile JVP
- Mechanical Compression: Stridor (Tracheal Compression), Tracheal Deviation, Hoarseness
- Nerve Compression:
- Horner’s Syndrome (Unilateral Ptosis, Anhydrosis, Miosis, Enophthalmos, Laryngeal Hoarseness)
- Unilateral Phrenic Nerve Paralysis ➔ Unilateral Diaphragm Paralysis ➔ Asymmetrical Chest Expansion.
- Signs of Causes:
- ↑Thyroid Gland (Retrosternal Goitre)
- Virchow’s Node (R-Supraclavicular Lymphadenopathy) for Lung Cancer.
- Other:
Lung Cancers:
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Often Asymptomatic..But may ➔ :
- Fever, Night Sweats, Weight Loss, Fatigue
- Dyspnoea
- Cough (+/- Haemoptysis) (+/- Wheeze if Bronchial involvement)
- (Don’t Forget +/- Paraneoplastic Syndrome)
- Hypercalcaemia (↑PTH)
- Hyponatraemia (↑ADH)
- Cushing’s (↑ACTH)
- Carcinoid Syndrome (↑Serotonin)
- Gynaecomastia (↑Gonadotrophins)
- Often Asymptomatic..But may ➔ :
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Vitals:
- Fever, Tachypnoea (late stages)
- Other:
- General Signs:
- Anorexia, Clubbing, HPOA (Wrist Tenderness), Intrinsic Hand Muscle Wasting, Virchow’s Node (R-Supraclavicular Lymphadenopathy), Axillary Lymphadenopathy, Liver & Bony Tenderness (Metastases)
- If Apical (Pancoaste) Tumour ➔
- SVC obstruction ➔ Pemberton’s Sign (Facial Plethora)
- Sympathetic Nerve Compression ➔ Deficiency ➔ Horner’s Syndrome (Unilateral Ptosis, Anhydrosis, Miosis, Enophthalmos, Laryngeal Hoarseness)
- C8/T1 Nerve Lesion ➔ Intrinsic Hand Muscle Weakness & Wasting
- If Mesothelioma ➔
- Pleuritic Chest Pain
- Pleural Effusion
- Tender Ribs
- If Bronchocarcinoma ➔
- Wheezing (Partial Bronchial Involvement)
- Atelectasis (Complete Bronchial Obstruction)
- Haemoptysis
- General Signs:
- Signs of Causes:
- Smoker, Miner, Sand-Blaster, Builder,
- Vitals:
URTI:
- TYPICAL Symptoms/Presentation:
- Fever
- Sore-Throat
- Runny Nose, Sneezing, Hoarseness, Cough
- Sinus Headache
- +/- Non-Specific Viral (Fever, Malaise, Headache, Myalgia)
- TYPICAL Clinical Signs:
- Typical URTI Symptoms:
- Fever, Malaise, Headache, Cough
- + Specific Symptoms:
- Adolescent + Sore Throat + Lymphadeopathy = EBV (Glandular Fever)
- Toddler + Drooling Saliva = Epiglottitis (Haemophylis Influenza)
- Photophobia + Neck Stiffness = Meningitis (Eg. Nesseria Meningiditis)
- Arthritis + New Cardiac Murmur after 2wks = GAB-Strep Pharyngitis ➔ Rh-Fever/Rh-Heart Disease
- Hx of Recurrent Pneumonia + SOB = Cystic Fibrosis/Immunocompromised/Smoker
- SOB + Weight Loss = Tuberculosis (Mycobacterium Tuberculosis)
- Community Outbreak + Travel History = SARS (SARS-Associated Coronavirus
- Typical URTI Symptoms:
Thank You so Much. Happy Learning!!